Közönséges lábatlangyík
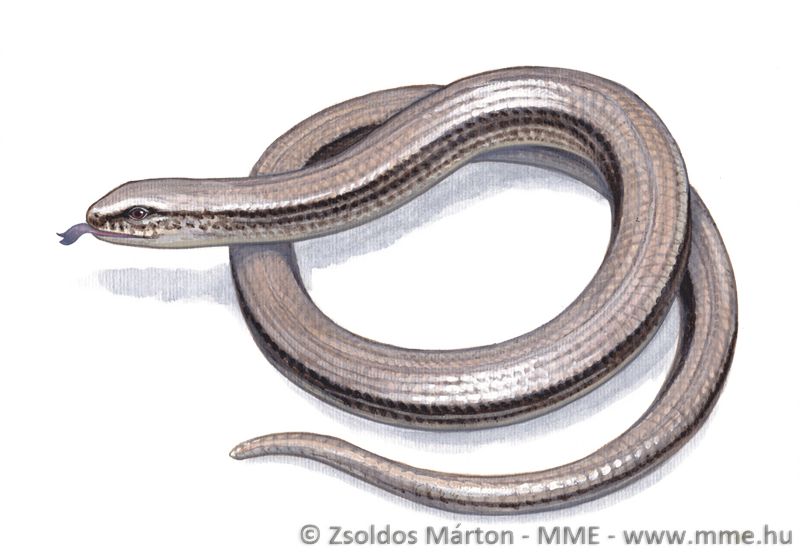


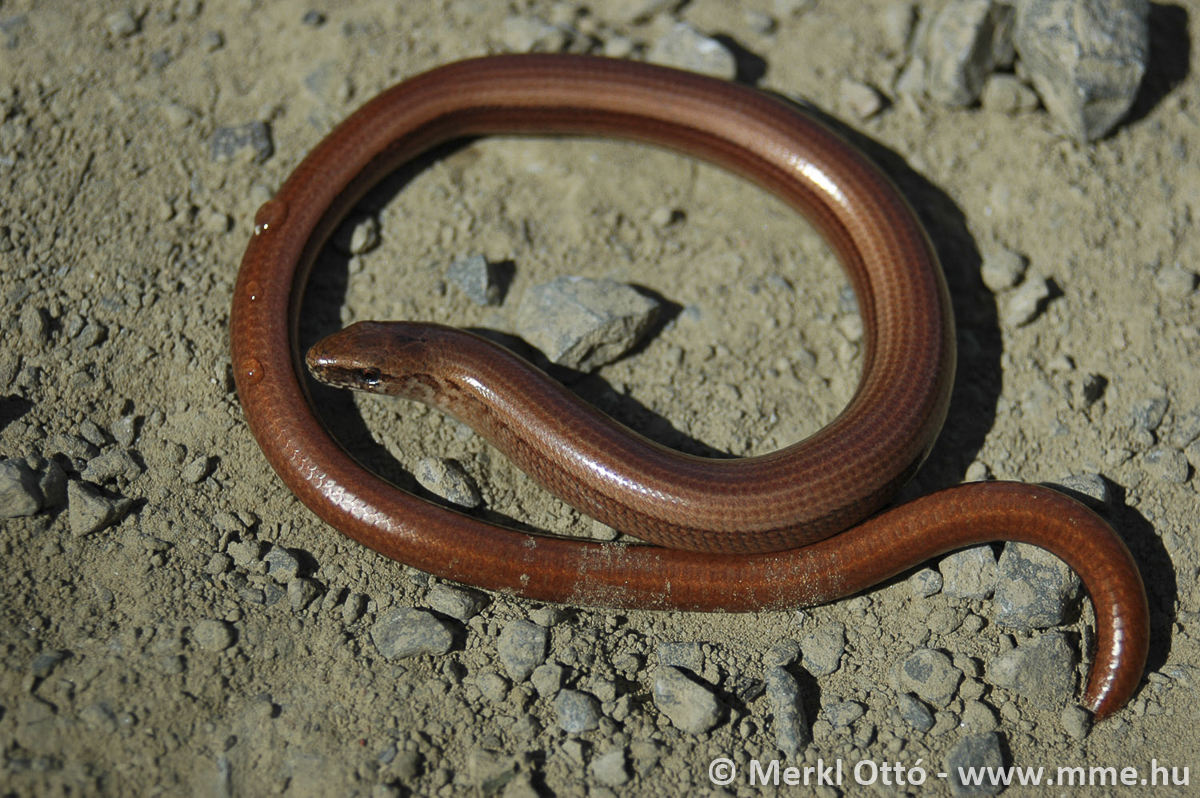
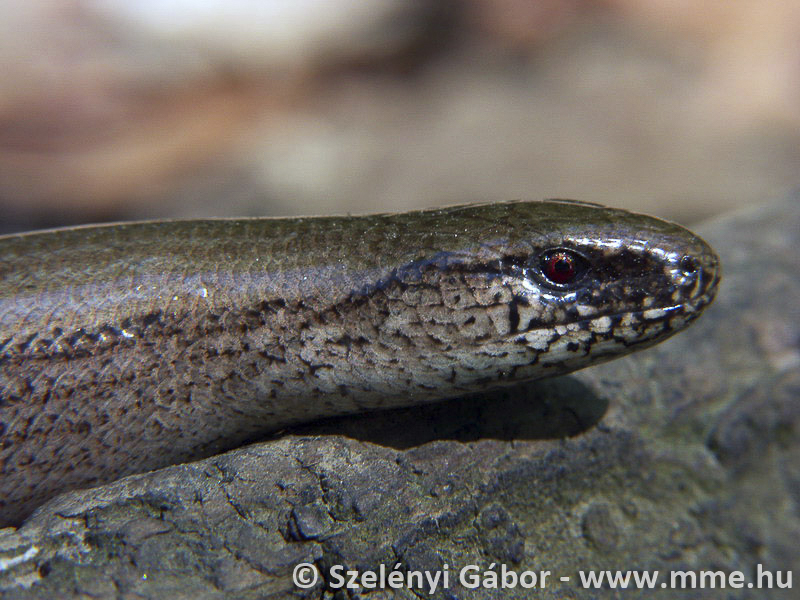
A közönséges lábatlangyík teljes hossza elérheti az 50 centimétert. Mivel nincs lába, amely támpontot adhatna, teljes hossza felét-kétharmadát kitevő farka távolról szinte elkülöníthetetlen karcsú testétől. Természetesen a kézbe vett lábatlangyíkon a kloáka elhelyezkedése pontosan megmutatja a farok kezdőpontját. A hasa gyakran sötétebb is, mint a farka alulsó oldala. Feje meglehetősen kicsi, alig különül el a testtől. Szeme ugyancsak kicsi, pupillája kerek, írisze bronzos vagy csillogó barna. A fejtetőn nagyméretű pajzsok találhatók. Testén a pikkelyek aprók (a gerincvonal két oldalán húzódó pikkelyek valamivel nagyobbak), finoman illeszkednek egymáshoz, emiatt a bőre látványra és tapintásra is sima. Az alapszín egyedenként változó lehet: fémesen csillogó szürke, ezüstös, rózsaszínes, de leggyakrabban a barna valamilyen bronzos árnyalata. Hasa általában sötéten pettyezett vagy márványozott, gyakran teljesen fekete. A nőstények mintázata eltér a hímekétől. Hátuk közepén két, gyakran egybe olvadó vékony sötétbarna vagy fekete csík fut. Testoldalukon sötét színű, széles, hosszanti sáv húzódik. A hímek testoldala általában nem sötét, hanem többé-kevésbe megegyezik a test többi részével. Bár a kék pettyek elsősorban a kékpettyes lábatlangyíkra jellemzőek, a közönséges lábatlangyík hímjei is gyakran viselnek égszínkék pettyeket. A fiatalok színezete markánsan eltér a felnőttekétől. Alapszínük aranysárga vagy ezüstös. Hátuk közepén jól látható sötét csík fut, bár előfordul, hogy hiányzik. Oldaluk és hasuk ugyancsak sötét.

A korábban egy fajnak tekintett „lábatlan gyík” (Anguis fragilis) mai ismereteink szerint 4 különböző fajt foglal magába: a közönséges lábatlangyíkot, A. fragilis, a kékpettyes lábatlangyíkot, A. colchica (Nordmann, 1840), a görög lábatlangyíkot, A. gracea Bedriaga, 1881, valamint a már sokkal korábban leválasztott peloponnészoszi lábatlangyíkot, A. cephallonica Werner, 1894. Kutatók felvetették, hogy az Appennini-félsziget lábatlangyíkjait is faji rangra kellene emelni. A rendszertani változás az új magyar elnevezésben is tükröződik, a lábatlangyík, mint génusznév egybeírandó. A legutolsó átfogó törzsfejlődéstani vizsgálatok szerint a Kárpát-medencében és így Magyarországon a közönséges és a kékpettyes lábatlangyík is előfordul. A két fajt tehát honlapunkon külön-külön mutatjuk be. A közönséges lábatlangyík genetikailag meglehetősen egyöntetűnek tűnik, alfajokat nem különítenek el. A lábatlangyíkot szokták törékeny gyíknak és népiesen kuszmának is nevezni.
A lábatlangyíkokat a felületes szemlélők gyakran tévesztik össze a kígyókkal. Ha azonban alaposabban szemügyre vesszük őket, egyáltalán nincs „kígyó jellegük”. Testük sokkal merevebb, ezért mozgásuk is kevésbé kecses, mint a kígyóké. Pikkelyeik aprók és szorosan illeszkednek, ezért testük a kígyókénál láthatóan és tapintva is sokkal simább. Fejük kicsi, szemben a kígyók nagyobb, nyaktól jobban elkülönülő fejével. A lábatlangyíkok szeme apró, és szemhéjuk lecsukható, míg a kígyók nem tudnak pislogni.
A fiatal lábatlangyíkokat a tapasztalatlan szemlélő esetleg összetévesztheti a pannongyíkkal. A pannongyíknak azonban vannak lábai, színe bronzos, szemben a fiatal lábatlangyík aranysárga színével. A pannongyík nem visel a háta közepén sötét csíkot. A két faj élőhelye markánsan eltér, de élőhelyeik határain mindkettőjükkel találkozhatunk.
Hazánkban a két lábatlangyíkfajt viszont nem könnyű megkülönböztetni. Támpontot elsősorban előfordulási helyük adhat (lásd a Hazai elterjedés című fejezetet). A közönséges lábatlangyík ritkábban visel kék pettyeket, de ha igen, azok általában kisebbek, mint a kékpettyes esetében, és többnyire csak a hímeken vannak jelen. Néhány további megkülönböztető alaktani bélyeg, amely segíthet a két faj elkülönítésében: a közönséges lábatlangyík hallónyílása alig látható (a kékpettyes lábatlangyík hallónyílása jól látható). A közönséges lábatlangyíknál az ún. orrnyeregpajzs és a homlok pajzs nem érnek össze, (a kékpettyes lábatlangyíknál többnyire érintkeznek). A közönséges lábatlangyík testének középtáján 24-26 hátpikkelysor található (a kékpettyes lábatlangyíknál 26-30).
Hazai elterjedés A közönséges és a kékpettyes lábatlangyík Magyarországon túlnyomórészt parapatrikus, azaz elterjedési területük érintkezik, de nem fed át. A határvonalat a két faj között a Duna képezi. A közönséges lábatlangyík a Dunántúlon, a kékpettyes lábatlangyík a Dunától keletre található meg. Az előzetes genetikai vizsgálatok eredményei alapján azonban a Dunazug-hegységben és a Börzsönyben hibridzónát alkotnak. A közönséges lábatlangyík tehát a Dunántúl domb- és hegyvidékein fordul elő, de léteznek síkvidéki állományai is.
Készült az Országos Kétéltű- és Hüllőtérképezés Program honlapjára beérkezett adatok felhasználásával.
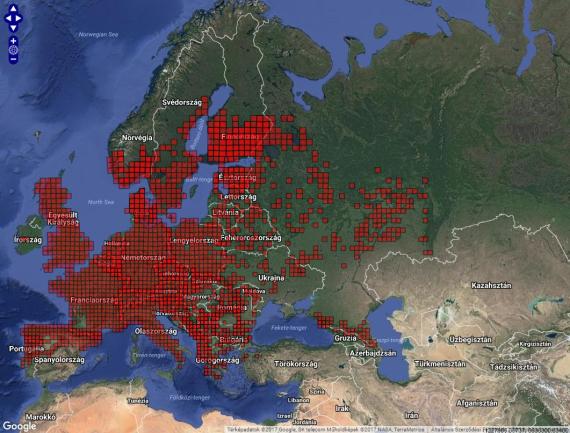
Világelterjedés A közönséges lábatlangyík a Pireneusi-félsziget déli részét és a Földközi-tengeri szigeteket leszámítva egész Délnyugat- (De lásd az Appennini-félszigetre vonatkozó megjegyzést a Taxonómia című fejezetben!) és Nyugat-Európában megtalálható. Írország kivételével benépesíti a Brit-szigeteket, valamint Skandinávia déli részét. Keleti és délkeleti irányban elterjedt Csehországban, Lengyelország nyugati felén, Nyugat-Szlovákiában, Magyarországon a Dunántúlon, illetve a Balkán északnyugati részein. Elszigetelt állománya ismert az északkelet-görögországi Trákiában, illetve Délnyugat-Bulgáriában.
A lábatlangyík faj-komplex európai elterjedése. Készült az Európai Herpetológiai Atlasz honlapja alapján.
A lábatlangyíkok elsősorban a részlegesen zárt, erdei vagy cserjés vegetációhoz kötődnek. Ebből kifolyólag többnyire hegy- és dombvidékeinken fordulnak elő, de természetes állapotban fennmaradt síkvidéki erdeinkben vagy lápok, árterek peremén is fellelhetők. Leggyakrabban erdőszéleken, erdei tisztások szegélyein, turistaösvényeken találkozhatunk velük, ahova gyakran fekszenek ki sütkérezni. Fontos számukra a búvóhelyek (korhadó farönkök, kőrakások, kőkerítések, rágcsálójáratok) jelenléte. Élőhelyeik közelében kertekbe is bemerészkednek.
Mivel csak a közelmúltban szereztünk tudomást a két hazai lábatlangyíkfaj rendszertani különbözőségéről, biológiájuk különbségeiről nincsenek ismereteink. Jelenlegi tudásunk alapján a következőekben leírtak mindkét fajra jellemzőek. A lábatlangyíkok többnyire reggel és alkonyatkor aktívak. Eső után gyakrabban jönnek elő, ilyenkor napközben is könnyen szem elé kerülnek. A reggeli órákban sütkérezéssel érik el „üzemi hőmérsékletüket”. Általában lassú mozgásúak, de ha felmelegszenek, gyors menekülésre is képesek. Táplálékukat ugyancsak lassú mozgású gerinctelenek képezik, elsősorban földigiliszták, meztelencsigák és rovarlárvák, de mindent elfogyasztanak, amit, egyébként meglehetősen kicsi állkapcsaikkal meg tudnak ragadni és le tudnak nyelni. Több olyan eset is ismert, amikor kifejlett lábatlangyík elfogyasztotta újszülött fajtársát. A párzási időszak április végére, májusra esik. A hímek vetélkednek a nőstényekért. Párosodáskor állkapcsukkal fogva tartják a nőstény nyakát. Mindkét faj elevenszülő. A nőstény augusztusban vagy szeptemberben hozza világra 2-12, farokkal együtt 8-12 cm hosszú kicsinyét. A fiatalok rejtettebb életmódjuk és apró termetük miatt sokkal ritkábban kerülnek szem elé. A lábatlangyíkok október közepétől hibernálni vonulnak. A telet farönkök, gyökerek alatt, rágcsálójáratokban vagy sziklahasadékokban vészelik át.
Ha megfogják őket, a lábatlangyíkok nem harapnak, de ürülékükkel összekenik támadójukat. Más hazai gyíkokhoz hasonlóan képesek ledobni farkukat, ezért jobb, ha nem próbálkozunk megfogásukkal.
A lábatlangyíkoknak számos ellensége van. Szinte minden ragadozó, ami hajlamos hüllőket fogyasztani (kígyók, emlősök, madarak), zsákmányul ejtheti őket. Valószínűleg fontos zsákmányát képezik a sokszor azonos élőhelyen előforduló erdei sikló fiataljainak és a rézsiklónak.
A lábatlangyíkok Magyarországon viszonylag gyakoriak a számukra megfelelő élőhelyeken. Sajnos, sokan tudatlanságból kígyónak vélve agyonverik őket, annak ellenére, hogy a kígyófajaink is védettek. A hazai populáció két fajra osztása azonban azt jelenti, hogy hazánk területén osztoznak, elterjedési területük tehát egyenként jóval kisebb, csak az ország valamelyik felére szorítkozik. A Berni Egyezmény III. függelékébe tartoznak. Magyarországon a közönséges lábatlangyík – mint minden hüllő és kétéltű – védett. Természetvédelmi értéke: 25 000 Ft.
Beshkov, V. 1966. Investigations on the systematics and distribution of the slow worm (Anguis fragilis L.) in Bulgaria. Bulletin de l'Institut de Zoologie et Musée, 21: 185-20.1 (bolgár nyelven orosz és német nyelvű összefoglalóval)
Bryant, S.V. & Bellairs, A.d’A. 1967. Tail regeneration in the lizards Anguis fragilis andLacerta dugesii. Journal of the Linnean Society (Zoology), 46: 297-305.
Capula, M. & Luiselli, L. 1993. Ecology of an alpine population of the Slow Worm, Anguis fragilis Linnaeus, 1758.Thermal biology of reproduction (Squamata: Sauria: Anguidae). Herpetozoa, 6: 57-63.
Capula, M., Luiselli, L. & Anibaldi, C. 1992. Biennial reproduction and clutch parameters in an alpine population of the slow worm, Anguis fragilis Linnaeus, 1758 (Squamata, Sauria, Anguidae). Herpetozoa, 5: 95-98.
Çiçek, K., Tayhan, Y., Hayretdağ, S., Ayaz, D. & Tok, C. V. 2011. A case of cannibalism behavior of the Slow worm, Anguis fragilis (Reptilia: Anguidae) in Turkey. Bihareain Biologist, 5: 76-77.
Davies, M. 1967. A case of Anguis fragilis devouring newly-born young. British Journal of Herpetology, 4:20.
Ferreiro, R. & Galán, P. 2004. Reproductive ecology of the slow worm (Anguis fragilis) in the northwest Iberian Peninsula. Animal Biology, 54: 353-371.
Ghira, I., Nemes, S. & Rozsa, F. 1999. The ethogram of Anguis fragilis: feeding behaviour. Nymphaea. Folia Naturae Bihariae, 27: 153-159.
Gregory, P.T. 1980. Physical factor selectivity in the fossorial lizard Anguis fragilis. Journal of Herpetology, 14: 95-99.
Gvoždík, V., Jandzik, D., Lymberakis, P., Jablonski, D. & Moravec, J. 2010. Slow worm, Anguis fragilis (Reptilia: Anguidae) as a species complex: Genetic structure reveals deep divergences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 55:460-72.
Lác, J., 1967. To the systematics of the slow worm (Anguis fragilis L.) and its distribution in Slovakia. Biológia (Bratislava), 22: 908-921. (szlovák nyelven német és angol összefoglalóval)
Luiselli, L. 1992. The diet of the Slow Worm, Anguis f. fragilis Linnaeus, 1758, in the Tarvisio Forest (Carnic Alps, NE Italy) (Squamata: Sauria: Anguidae). Herpetozoa, 5: 91-94.
Macey, R.J., Schulte II, J.A., Larson, A., Tuniyev, B.S., Orlov, N., Papenfuss, T.J., 1999. Molecular phylogenetics, tRNA evolution, and historical biogeography in anguid lizards and related taxonomic families. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 12: 250-272.
Patterson, J. W. 1990. Field body temperatures of the lizard Anguis fragilis. Amphibia-Reptilia, 11:295-299.
Pedersen, I., Jensen, J. & Toft, S. 2009. A method of obtaining dietary data for slow worms (Anguis fragilis) by means of non-harmful cooling and results from a Danish population. Journal of Natural History, 43: 1011-1025.
Shcherban’, M.I. 1976. To the intraspecific systematics of the slow worm (Reptilia, Sauria, Anguis fragilis L.). Sborn. Trud. Zool. Mus. (Kiev), 36: 81-83 (orosz nyelven).
Stumpel, A.H.P. 1985. Biometrical and ecological data from a Netherlands population ofAnguis fragilis (Reptilia, Sauria, Anguidae). Amphibia-Reptilia, 6: 181-194.
Voipio, P. 1962. Multiple phaneromorphism in the European slow-worm (Anguis fragilis) and the distributional and evolutionary history of the species. Annales Zoologici Societatis Zoologicae-Botanicae Fennicae 'Vanamo, 23: 1-20.
Wermuth, H. 1950. Variationsstatistische Untersuchung der Rassen- und Geschlechtsmerkmale bei der Blindschleiche (Anguis fragilis Linné). Deutsche Zool. Zeitschrirt, 1: 81-121.